Every second, Google process 100,000+ searches. That means that this year there will be over 2 trillion Google searches. That’s a lot of Googling! It also means that as a digital marketer it is more important than ever to understand Google SERP Features and how they affect your webpage.
Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) simply contains a list of results without any variation or rich elements, geo-location or e-commerce shopping listings. It was a search directory, raw, clean, and simple. Whilst this was probably far more efficient and arguably less susceptible to those trying to game the system, it definitely made it harder to distinguish your business from others. Now, there are a variety of ways businesses can optimise their websites to increase visibility. Currently, Google has 16 SERP Features that provide more detail than standard results. The type of question searched will influence the SERP Feature that will be shown. Here, we will go through some of the top SERP Features SEO Sydney consider important for our clients.
FEATURED SNIPPETS
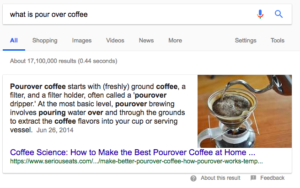
Users go to Google to find the answer to a question. Featured Snippets are Google’s way to quickly answer that question. Featured Snippets are often referred to as position #0 because it appears above the #1 ranked organic result. As shown below, Features Snippets feature a title, an answer extracted from a website, and the link to the website it took the information from.
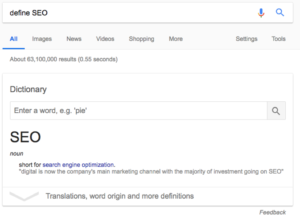
Featured Snippets are different than direct answers. Direct answers are for more factual inquiries, such as dictionary definitions, weather, or calculations.
Why are Featured Snippets important? For one, they can help the credibility of your website and can help establish brand authority. It is also the first result to appear on the page, above traditional organic results. Usually, Featured Snippets will also be in the top 5 organic result on the page as well, giving the business two listings on the first page.
It’s natural to think that Featured Snippets could take away from click-through rates, but there have been mixed results. While some SEO companies claim that it doesn’t hurt CTR, others have shown it can decrease CTR. One study showed a 18.5% decrease in clicks compared to Google search results without Featured Snippets. This may be because those looking for a quick answer get their answer without going any further. For example, if you wanted to know what pourover coffee was out of simple curiosity, the Featured Snippet would answer that question.
On the other hand, Hubspot found that CTR increased more than 114% when it appeared as the Featured Snippet. This could be attributed to users wanting a more in depth answer to their question. Consequently, clicking through to the webpage.
This is an important difference to note. Businesses should be aware of content that is more likely to lead to a click-through. As a business, you want to ensure your content surpasses simple curiosity and encourages users to dive deeper for more information.
How do you rank?
Your business should already be ranking on the first page, preferably in the top 5. But to get featured you essentially need to do one thing: answer the question. This means it’s important you have quality content, both good for SEO and informative to the audience. This can be difficult to do, but not impossible.
Format your content in a Google-friendly matter by breaking up paragraphs. This helps Google take a snippet of your content and display it in the Featured Snippet. The standard length of a Featured Snippet is around 40 – 50 words, so making your summary around that length will help. By writing informative content and being clear as to what question you are answering, you will help Google understand your content.
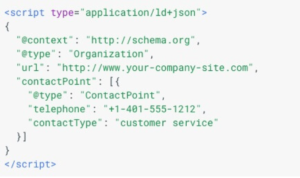
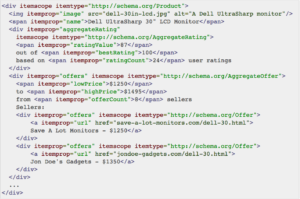
Finally, using Schema Markup helps tell Google what your content means. Schema markup is not required for Featured Snippets, but it definitely doesn’t hurt. If you do use it, it looks something like this:
Schema Mark Up
Schema markup is code you use to help Google crawl your website, so it can return more accurate results for users. Luckily, you don’t need to learn how to code to use schema markups. Schema.org is the go-to website for schema markup and all of the code required is already made for you. If you’re curious, Schema.org offers a full list of items that can be markedup (Hint: it’s a lot).
REVIEWS
A wall of text on a results page is boring. Reviews allow the user’s attention to be drawn toward a particular result on the page. Reviews are most commonly shown as a star rating under the URL and above the description of the search result. They’re usually used for recipes, products, events or businesses.
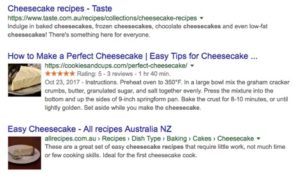
Reviews can help your business by increasing click-through rates (especially if you have a 4 or 5-star rating). After a Google search for “Cheesecake recipe” the top three search results appear. Only one features a Review, and as you can tell, the eye is drawn toward this result. Even though Taste.com.au is the #1 organic result on the page, users are more inclined to click on the second link.
Google doesn’t share its rules for Reviews and which results are eligible for them to show up. But, it is believed having positive reviews can help your webpage move up in ranking over time. At very least, people are more likely to click-through to a website because of their trust in ratings, which would eventually move your webpage up in the rankings.
How do you rank?
To rank, you’ll need reviews of your product or website. Try not to only take reviews from websites such as Yelp. Apparently, Google prefers the reviews to be visible on your site as well.
You can use a plugin to gather reviews from customers after their recent purchases. Once you have your (positive!) customer reviews you need to make sure Google can interpret the data on your webpage. This can be done by using schema markup. The markup would look something like this:
You’ll need to provide Google details about your organisation (location, hours, phone number, etc.) and what webpages you want to include star ratings. Here’s the catch – it’s up to Google if it displays your ratings. Because the ratings are supposed to reflect a product or service, try to be selective on which pages you put a star rating on.
SITE LINKS
Site links are additional links under the main URL for a brand’s website. Occasionally, it will include a search box users can use to immediately search within the website. Site links usually appear in a search for a specific brand and Google decides on which site links to display, meaning it’s not up to you on what to feature.
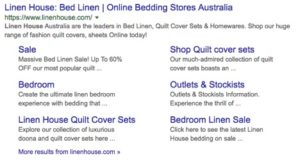
If you search for Linen House, the firs result is Linen House with site links. Directly under the main URL, you can reach a variety of pages within the website.
Even though your business can’t choose the links shown, site links still come with benefits. For one, they take up more search page real estate. On mobile phones this can be the entire screen, making users scroll down before they see other options. This increases the chances users will click through to your site instead of a competitor’s. It also allows users to directly reach the page on your site they are looking for, without a landing page they might not need. One thing to keep in mind is that the site links displayed will serve as a new landing page for customers. Therefore, it’s important your landing pages provide a good first impression to customers.
How do you rank?
Although Google has control over which pages it chooses to display, it has provided a couple of tips on how to influence which site links appear. First, it’s important to rank #1 in your brand name. Site links only appear for top searches (so it’s important you’re a top result). For example, Linen House was a client at SEO Melbourne and our SEO Services produced keyword optimised content, allowing it to hit #1. This led to it appearing with sitelinks. Your website also needs to be easily navigable and structured in a way that allows Google’s algorithm to find quality site links.
VIDEOS
Videos have become increasingly important when it comes to online content. Video SERPS are video snippets that appear among the organic search results. Like other results, they have a title and a description, but also include a thumbnail video. Most often they link back to YouTube.
YouTube is becoming more and more popular as a search engine. And because Google knows that (and owns it), it will select videos it believes important for users to see.
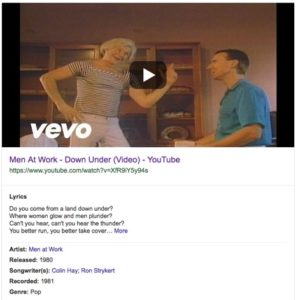
If Google is certain a video is relevant to the SERP, it will feature a larger thumbnail with additional information, such as lyrics, release date and genre.
Video SERPS are helpful because they draw the eye away from the block of text that makes up the other search results.
How do you rank?
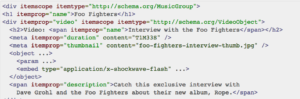
Video schema markup is required for Google to recognise your video content. By providing details on the video, such as the URL, duration, upload date and description, Google can recognise the content of your video and use your video in the organic search results. But even then, Google can choose if it wants to use your video in the results. Again, a video schema markup looks something like this:
RELATED QUESTIONS
Related questions are additional questions Google has generated because it believes they may be related to the search query. The questions expand down into a box that looks similar to a Featured Snippet, with an excerpt from a website and a link to the webpage. Related questions can be mixed into organic results, but often appear after a Featured Snippet.
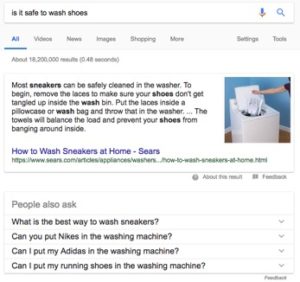
Related Questions are helpful for the user because they may not know the question they should ask for the answer they need. If you ask “Is it safe to wash shoes?” Google’s algorithm generates similar questions related to washing shoes under the Featured Snippet. Rather than the user finding out that it is, in fact, safe to wash shoes and starting a new Google search to find out how, the Related Questions section quickly directs the user to information on the best way to wash shoes.
How do you rank?
Related Questions are beneficial for your webpage because, like Featured Snippets, they may result in an increased CTR (although by not as much). Ranking for Related Questions is much the same as it is for Featured Snippets. Just like Featured Snippets, it is up for debate on if schema markup is beneficial for Related Question. But again, it certainly doesn’t hurt. Follow the same steps for Featured Snippets to try to obtain a spot in Related Questions.
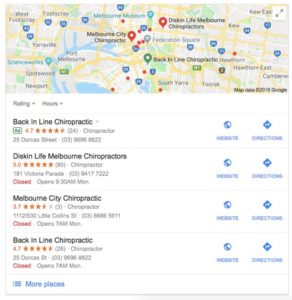
LOCAL PACKS AND LOCAL TEASER PACKS
Local Packs are shown when Google considers local businesses relevant for the search enquiry. For instance, if you Google “Melbourne Chiropractor” a map and a list of local businesses will show up in the SERP. The Local Pack includes reviews, hours, contact information, and a link to the website and directions via Google Maps. In this example, you also see Locals Packs can support ads.
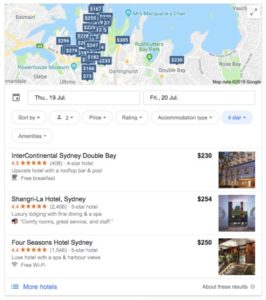
Local Teaser Packs are so similar to Local Packs you may not have realised there was a difference between the two. Local Teasers tend to feature hotels and restaurants in the area and offer slightly different information than a Local Pack. Local Teasers offer reviews, a short description, rates and an image of local businesses related to the search. It also offers the ability to sort results by price or rating. If you search “Luxury hotels Sydney” Google provides this Local Teaser. You can see a description of each hotel, its price, and a photo. It also allows you to select dates for your visit and sort by price, rating, and amenities.
When comparing the two, remember that Local Packs are for users wanting a quick answer for a service in their area. On the other hand, Local Teasers offer users more in depth results with the ability to search different criteria they may be looking for.
The benefit of being included in Local Packs and Local Teasers might seem obvious. Users looking for a particular service in their area will see your webpage as one of the top options in the area. Plus, if they are searching on their phone, Local Packs and Local Teasers usually take up the entire screen, requiring them to scroll down further to see other results. They also have good CTRs compared to results lower on the page. One thing to note with Local Teasers, unlike Local Packs, is that if the user clicks on your business (let’s say the Four Seasons Hotel Sydney) it doesn’t bring them to the business website. Instead, it directs them to Google Map results. This does lower the CTR for Local Teasers compared to Local Packs.
How do you rank?
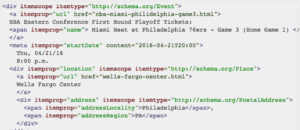
Similar to the other SERP Features, it’s important to already be one of the top search results on the page. Google takes the top three results and uses those for the Local Pack. Again, this involves having a well-structured, mobile-friendly website and positive ratings of your business. Part of this, of course, involves making sure Google knows where your business is located. Without your location, you are unlikely to make it to a Local Pack or a Local Teaser Pack. Example for schema mark up for business or event location is shown below:
KNOWLEDGE PANELS
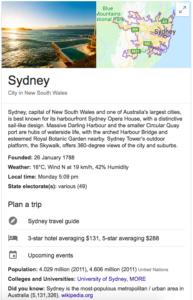
Knowledge Panels, also known as Knowledge Graphs, cover quite a few topics, including people, organisations, local businesses, media, and products. They show up on the right side of organic results and feature a photo, a short description and other relevant information. Knowledge panels appear in about one third of all queries on Google, suggesting that they’re important to know about. In the example below, a search for Sydney, Australia provides a knowledge panel with a variety of information the user may find helpful. This information is pulled from Google’s own data as well as other sources (Wikipedia is a common source).
One thing to keep in mind is that Google does not provide sources for the information it pulls for Knowledge panels. While the usefulness for users is high, it’s not necessarily the same for business owners. Having your own Knowledge Panel for your businesses can bolster both visibility and credibility, but it won’t necessarily drive higher CTRs, as it won’t link back to your webpage. That being said, Knowledge Panels can provide useful information such as your opening hours, ratings, and popular times. They can also link back to your social media sites. So while Knowledge Panels don’t directly help with CTRs, they can still benefit your business if you use them well.
How do you rank?
Similar to some of the other SERP Features, there is not guaranteed way to be featured. If you do want the best chance for a Knowledge Panel to feature your business then you need to use the correct schema markup, submit your business to Wikipedia and Google+, and verify any social media pages you have.
As mentioned, Knowledge Graph’s borrows information from Wikipedia to fill out business details. So without a Wikipedia page, Google can’t get that information about your business, therefore making it unlikely you will receive a Knowledge Panel. It’s a similar situation for Google My Business. Google My Business allows local businesses to update their local listings. Google’s Knowledge Panels uses this information to retrieve relevant information. Further, verifying your social media accounts allows Google to recognise you as the official representative of your business. This allows you to request changes to your Knowledge Panel.
One example of what part of your Schema Markup would look like is this:
Conclusion
SERPs make search results more accurate, more relevant and easier to find and the SERP Features discussed here are only a few of the many options Google has created. Optimising your website and ranking for SERP Features can help boost website traffic and CTRs, while also allowing users to quickly find relevant information to their search query.
SEO Sydney’s top tip: Regardless of the SERP Feature most important to your business, it’s important to stay on top of an ever-changing digital playground.